ETHZ – High Power Electronic Systems Lab
The research at the High Power Electronic Systems Lab (HPE) focusses generally on the design, modelling, and optimization of high power converter systems required for example in future energy distribution systems for integrating renewable energy sources or in electric mobility applications. A further research focus is on solid state pulse modulator systems for medical applications or accelerators as required for example by CERN or PSI.
In the area of battery systems, the High Power Electronic Systems Lab focusses on concepts for interconnecting batteries to the grid or drive train with highly compact and efficient power electronic converter systems. There, new concepts/topologies for power electronic converter systems are developed, but also comprehensive models (for existing concepts) are developed, which enable to fully optimize the performance of the converter system with respect to for example power density and/or efficiency. An example for such an optimized system is given below, where a 50kW dual-active bridge converter with an outstanding power density is shown, which is used in traction applications.
The High Power Electronic Systems Lab is cooperating in the following areas:
- Development of new concepts for power electronic converters interfacing batteries
- Development of new concepts for grid-level energy storage systems
- Modelling of converters including models of battery systems for optimization of
- Power density
- Efficiency
- Life time
- Costs
- …
- based on single operating points or mission profiles.
-
- Design and testing of prototypes for validation of concepts and models
Lab infrastructure
The Laboratory for High Power Electronic Systems is equipped with six medium voltage, high power test cells each with a floor space of approximately 25m2. The cells can be combined for larger test set ups. In the laboratory, the following sources are available:
- 400VAC / 250kW
- 400/0..800VAC / 250kW
- 25kVAC / 250kW
- 35kVDC / 250kW
- 2kVDC / 100kW (bidirectional)
- 400V Arbitrary AC Source (5kHz/100kW)
Furthermore, a water cooling with a heat removal capacity of 150kW and an air cooling system with a total power of 60kW are available in the cells. In order to move the test systems a crane is installed.
Juergen Biela
ETH Zurich
High Power Electronic Systems
ETL F16
Physikstrasse 3
8092 Zurich
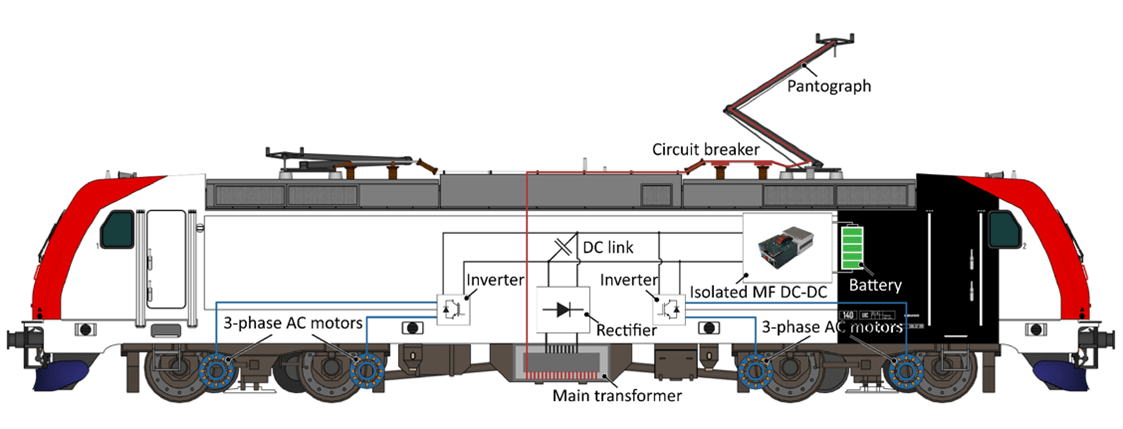
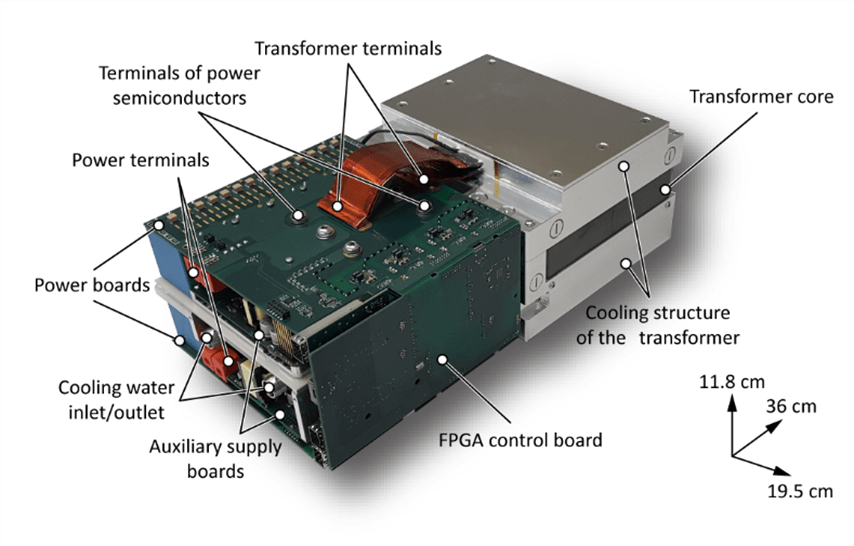
Example: Highly compact, isolated 50kW battery interface based on a dual active bridge for traction applications.
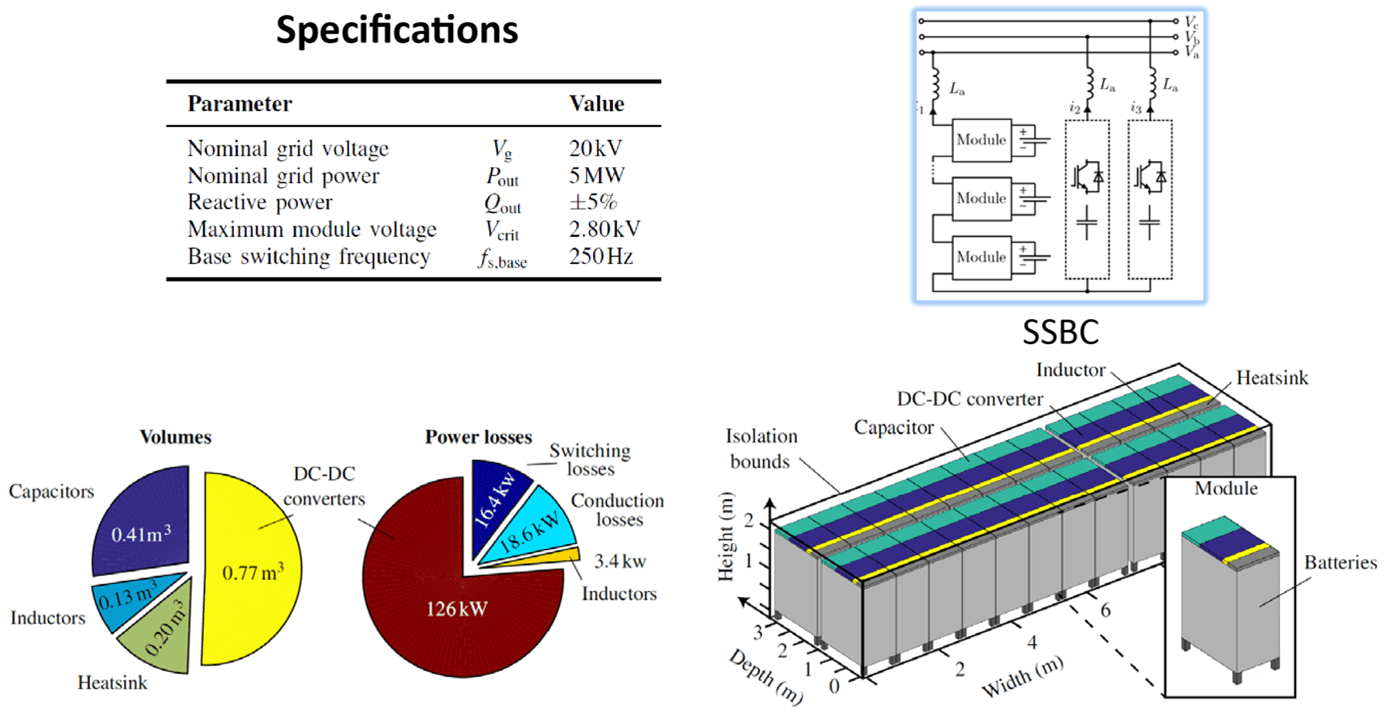
Example of a concept for a battery energy storage system on the medium voltage level in the distribution grid.